How to work with China education companies & Agents?
If you want to recruit international Chinese student … you can think of collaborate with Chinese education companies & agents.
Whay Chinese students check when choosing a university?
Reputation of the university of course.
Chinese student 64% consider quality of teaching the most important aspect of choosing an university. Reputation of the School & university really matter for them. They value practicality and believe that a university should be able to offer them an innovative outlook on the business world and new technologies. Employability is the second most important concern. 52% of students believe that a degree does not guarantee success in their chosen career. Employers are looking for universities that continue to innovate and develop, and that produce graduates who are able to meet their specific needs. 72% of students believe that studying abroad has the greatest benefit. This will give them a competitive edge when they return to the Chinese market.

What are some of the drawbacks to the Chinese higher education system.
China doesn’t have top-notch universities because its higher education system does not allow them enough freedom. Local colleges lack moral and academic essence. “China’s university spirit is truly lost.” It is a reflection on the entire society that has lost its way in utilitarianism. It is in a state spiritual dehydration”, says Yang Yuliang (Chancellor at Fudan University). The majority of tutors at Chinese universities focus on passing exams and not academic research.
Why would Chinese students choose to study abroad?
China is the largest student exporter in the globe, with more than 500.000 Chinese students studying abroad in 2015. Chinese families are known to have an influence on the education choices of their children. 51job.com recently conducted a poll that showed that most parents would prefer their children to study abroad. According to 51job.com, 76.8% of the 607 parents that took part in the survey said they would send their children abroad for a degree, even though the tuition and living expenses could reach 1 million Yuan (US $163,000.111). Caixin, a Chinese economics magazine, reports that students returning to China with a foreign bachelor’s degree earn nearly 5,000 yuan per monthly. This is almost double the starting salary for a Chinese graduate, which stands at around 2,443 Yuan. The United States, Canada, Japan, United Kingdom, and Japan are the top choices for Chinese students.
A US$40 billion market
Chinese international students spend more than US$40 billion each year in foreign countries, which includes tuition and living expenses.

Will national universities meet international standards and reduce the need to travel overseas?
The top 100 annual Asia Universities Rankings also included 18 schools from China, which is a 20% increase over last year. This was a major boost for China’s higher education system. According to Daxue Consulting the rise in quality teaching at national universities will reduce the need for students to travel overseas. However, this process can be very difficult and time-consuming. Chinese millennials will continue looking abroad until this happens.
Education is becoming increasingly important in China
Education is becoming increasingly important in China due to the rapid economic development. Our client was interested to enter the Chinese market through its educational offering. Daxue Consulting provided an overview of the Chinese school system and set out a five-year plan to develop the client’s idea.

Education Agencies & companies in China.
First, familiarize yourself with the work of Chinese educational consultancies and students recruitment agencies
- Agents help students determine a study abroad destination location i.e. If a destination or institution is not yet chosen, agents can help students determine the best location.
- Select the right university, college, institution or school for you.
- Apply for tuition programs or academic degrees. Short term programs; such as winter/summer camps, subject-specific training classes or other for-credit and non-credit programs, abroad.
- Assist them in the application process. Agents are chosen based on their reputation. Having the right partners can make all the difference in helping students find the best options.
Identify the goals of your institution and communicate these with potential agents
Learn about your agents and what they are looking for from your relationship with them
Identify the current problems in your institution and decide if they should be addressed internally or by agents.

Education Fairs & Events in China
Events and fairs are great ways to meet potential students. Here is a list containing the organizations that host fairs for Chinese student recruiting.
Information about upcoming tours can be found under the Resources tab in our article Upcoming recruitment fairs in China.
IT hosts both virtual and face-to–face recruitment fairs. It also offers tours to undergraduate and postgraduate institutions in order to meet East- and Southeast Asian students. China Education Association for International Exchange, (CEAIE).
Since 2000, the China Education Expo (CEE), hosted by CEAIE, has been held every year. The CEE recruitment fair will be available online for international institutions starting in 2021.
Annual University Discovery Weeks are hosted by Cialfo for parents, students, counselors, and other stakeholders in China, South Asia and the rest of the world.
AEO Tour hosts virtual fairs that allow college and university representatives to meet students from East Asia and Southeast Asia.
How to partner with Chinese Agents
Most Chinese students apply to foreign institutions through education agents. An agent network that is reliable can help increase the number Chinese applicants. Many schools don’t know where to begin because there are so many agents in China. These sites will help you find reliable, high-quality agents.
Use a Chinese Website can really give you credibility

Visibility on Baidu is the key in China
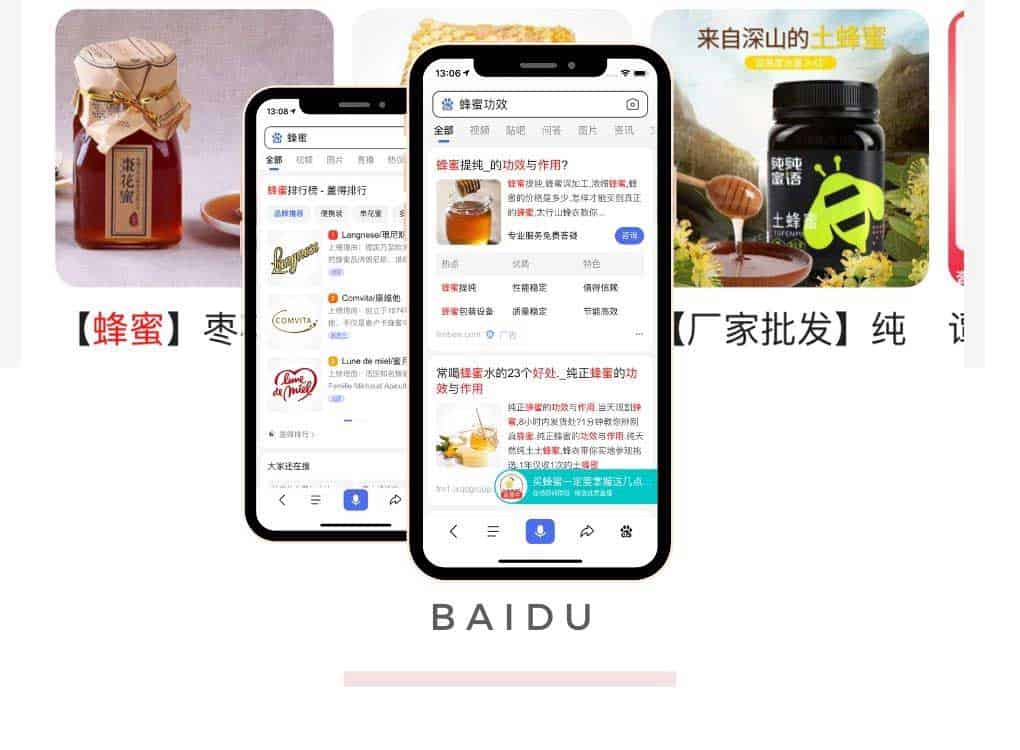
Communicate on WeChat is so important in China
*

Use EPR, online media to promote your school & university

If you want to launch a digital marketing campaign in China, feel free to contact our education expert.
China’s education: new policy & strategies
Global context, labour market trends, and official policies. China’s role in the global education market. The global education market is growing rapidly as students, educators, and content move more widely, and there are more public and private providers. Transnational education flows are increasing, but traditional English-speaking destinations countries like Australia may see their enrolment drop due to increased capacity and better language training in the source countries.
This could be because of competition from other non-traditional destinations. China has become a major player in the global education market, not only as a source of international students but also as a destination. China is making an effort to attract more international students, even though the number of Chinese students abroad is still substantial. China is the sixth-largest destination for transnational education in the world and has an increasing stake in education policy discussions. China is making an effort domestically to address the issues that hinder its education system’s appeal.
Higher demand for higher education in China
China’s economy, labour market and demand for higher education. China’s economic boom has created unprecedented demand. Private enterprises are driving the fastest growth and increasing incomes through diversification and expansion of the Chinese economy.
The accession of China to the WTO in 2001 has further integrated its economy into global trade patterns. Despite the rapid expansion of China’s higher education system, there is still a large gap between the needs of the job market and academic or vocational preparation. Employers complain about a lack in basic skills such as communication, interpersonal skills and functional skills. While the economy is growing rapidly, policymakers are becoming more concerned about unemployment.
Therefore, job creation will be a top priority for government. Particular employment problems will be faced by the four million-strong 2006 graduating class from higher education. The unemployed are also growing due to the demobilisation of soldiers, rural migrants and workers in state-owned enterprises (SOEs) who have been laid off.
Over the next five-years, there will be a high demand for labour in engineering, sales, marketing, finance and commerce. Employers expect a rising demand for restaurant and hotel staff, researchers, designers, production operators, and designers. 2 C. China’s education policy priorities China will see its college-age population reach 125 million people in 2008. This number will then decline to 69 millions by 2050.
China has made significant investments in education over the last decade to improve its global competitiveness. China’s number of post-secondary education institutions has increased rapidly. China’s gross enrollment rate, which was 13% in 2006, is expected to increase to 22% by 2010. China is developing its own elite universities and is not only trying to increase access to education. Beijing encourages a select few to join alliances with foreign institutions in addition to huge increases in funding.
The education bureaucracy has been streamlined by the government. The Ministry of Education has given up significant budgetary and oversight responsibility. Vocational education was previously under the Ministry of Labour and Social Security. The MoE will now manage new expansion.
The government has opened up the education sector to private and international providers in order to meet its capacity expansion and quality improvement goals. A variety of joint-venture agreements have been created with foreign partners. China’s universities are continuing to improve their quality through international recognition and accreditation. Any international education partner that can support them in this effort will be appreciated. China’s main policy priority is to increase its “human capacity” by providing vocational training and higher academic achievements.
Conflict of interest between Chinese and foreign partners is the most significant risk.
If the Chinese partner institution is motivated primarily by commercial goals, it could compromise the quality and effectiveness of the programme by lowering admission standards or cutting costs. The second half of the study program is to be held in Australia. Failure to obtain a 3 Australian visa could lead to an abrupt termination of this study programme without a certificate or degree. Concerns raised by foreign educators include the theft of intellectual property by local partners, and the use curriculum material that compromises the integrity the academic program.
Both parents and students felt that such programs were less attractive than studying abroad in surveys and interviews for this report. However, they see cost savings and other benefits. Employers are generally positive about these programmes’ quality. This study surveyed 123 employers and found that 60% believed that vocational training programs offered in China by foreign providers are a good way to train cross-cultural managers. R
Reports from both Australian and Chinese providers indicate that between 10% to 30% of pathway students are going on further study in Australia and other countries. Our interviewees stated that more pathway students would choose to study overseas, despite the high cost and English-competency requirements. While there have been some Australian companies that have made significant inroads in China, the margins seem to be low. The foundation programmes are designed to prepare students for university studies, often at a particular institution. These programs are designed to attract more Chinese students to study abroad, but they cannot pass English-competency exams. However, some students enroll in these programmes to improve their English skills and help them find employment. The study showed that foundation programs do not have a significant negative effect on the number Chinese students attending high school in Australia.
The success rate for students who go from foundation programs in China to top universities in Australia is low. Many students go on to study in other countries or institutions. Chinese partners are looking to offer foundation programs that allow students to choose from several institutions. It is believed that the MoE supports foundation programmes in China. Outlook. The outlook for foundation and pathway programmes is generally positive. These programmes will be more popular in China thanks to the involvement of professional bodies around the globe. As institutions offer pathways to cheaper campuses, such as those in Malaysia or Singapore, the impact of these lower-cost options will be clear. Foundation programmes are being established in China because of concerns about pastoral care and students’ ability to transfer from one culture and education system to another.
Opportunities in the Chinese international education market
This arrangement is a great opportunity for growth, but Chinese operators are unhappy with insufficient connections to Australian providers, lack of specific visa requirements and inconsistent results when applying for visas at different centres. China has little interest in standalone overseas English programs. This could be due to the fact that China has lower incomes than Japan and Korea. Both countries continue to send English-language students from Australia. It is evident that Australia’s products in this area aren’t well understood and that visa requirements are too complex.
Australia and its complex relationship with China
The Chinese government appeared to discourage career-oriented study of language in Australia. Many education agents in China are associated with English-language programs within their country and have little incentive or motivation to recommend foreign programmes. Outlook. Outlook.
The attractiveness of Australia as a tourist destination could be used to attract highly-qualified, wealthy students. Agents blame high-quality private schools for the decline in high school students coming to Australia to study. They also point out that there are high language and cost requirements and parental concerns. Agents also mentioned the perception that the English-competency requirement for visas was unpredictable.
They understood that high school students must take the IELTS test and that the Australian government has temporarily waived this requirement. This requirement is not required by most of Australia’s rivals. Private education providers have opened schools in China for expatriate students (the law requires that primary school pupils study the national curriculum), but such ventures are risky because there is a small market. Several educational bodies from five countries have signed licensing agreements with Chinese private schools.
Distance education. The Chinese government is making huge efforts to develop IT-based distance learning in order to meet the short-term demand for qualified staff and higher education. Chinese views of distance education are mixed. While the public views distance education positively due to its accessibility and low cost, many people have reservations about its quality and reputation. Employers generally view distance education positively, provided that the programs are offered by well-respected institutions. The fact that Chinese governments do not recognize degrees earned by foreign providers is a disadvantage. Outlook. As part of China’s overall growth in higher education, distance education will continue expanding.
Training and Education in China
Effective vocational training is a priority to prevent social unrest, especially among school-leaving students and young migrants from rural areas. The national government announced in




Every schools & universities want to collaborate with Chinese education companies
great information, but what should I do to work with Chinese education agent?
Where to start?
Working with education companies and agents in China can be a tactic to reach a large number of potential Chinese (rich) students and expand your educational business.
How to work effectively with Chinese education companies and agents:
Do your research: Before reaching out to education companies and agents in China, do your research and identify the ones that specialize in your field of education. Learn about their reputation, client base, and their preferred methods of communication.
Build relationships: Building personal relationships is crucial in Chinese business culture. Take the time to get to know the education companies and agents you’re working with and establish a relationship based on trust and mutual benefit.
Understand Chinese law 2021-2022: Chinese regulations for international education can be complex and frequently change. Stay up-to-date with the latest regulations and ensure that your educational programs comply with Chinese requirements.
Customize your program: Chinese education companies and agents may have different expectations and needs than those in other countries. Customize your approach and tailor your marketing materials and communication to fit their preferences.
Be patient: Building a successful relationship with education companies and agents in China takes time. Be patient, persistent, and flexible in your approach.
Provide support: Once you’ve established a relationship with education companies and agents in China, provide them with the necessary support to ensure the success of your educational programs. This may include providing training, marketing materials, and ongoing support.